Delegated Staking
Delegated Staking on the Endless Blockchain
We strongly recommend that you read about Staking first.
Delegated staking is an extension of the staking protocol. A delegation pool abstracts the stake owner to an entity capable of collecting stake from delegators and adding it on their behalf to the native stake pool attached to the validator. This allows multiple entities to form a stake pool that achieves the minimum requirements for the validator to join the validator set. While delegators can add stake to an inactive pool, the delegation pool will not earn rewards until it is active.
Delegation pools are permissionless and anyone can add stake. Delegation pools cannot be changed to stake pools once it's created or vice versa, though it can be removed from the validator set and assets withdrawn. For full details of the stake pool, see Staking
For the full delegation pool smart contract, see delegation_pool.move
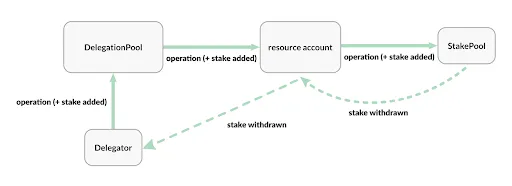
Unlike a stake pool, a delegation pool can be initialized with zero stake. When initialized, the delegated stake pool is owned indirectly via a resource account. This account will manage the stake of the underlying stake pool on behalf of the delegators by forwarding their stake-management operations to it (add, unlock, reactivate, withdraw) while the resource account cannot be directly accessed nor externally owned.
See full list of Delegation Pool Operations
 image
image
There are four entity types:
Owner
Operator
Voter
Delegator
Using this model, the owner does not have to stake on the Endless blockchain in order to run a validator.
How Validation on the Endless blockchain works
Owner
The delegation pool owner has the following capabilities:
Creates delegation pool
Assigns operator for the delegation pool
Sets operator commission percentage for the delegation pool
Assigns voter for the delegation pool
Operator
A node operator is assigned by the pool owner to run the validator node. The operator has the following capabilities:
Join or leave the validator set once the delegation pool reaches 1M EDS
Perform validating functions
Change the consensus key and network addresses. The consensus key is used to participate in the validator consensus process, i.e., to vote and propose a block. The operator is allowed to change ("rotate") this key in case this key is compromised.
The operator receives commission that is distributed automatically at the end of each epoch as rewards.
Voter
An owner can designate a voter. This enables the voter to participate in governance. The voter will use the voter key to sign the governance votes in the transactions.
Governance
This document describes staking. See Governance for how to participate in the Endless on-chain governance using the owner-voter model.
Delegator
A delegator is anyone who has stake in the delegation pool. Delegators earn rewards on their stake minus any commissions for the operator. Delegators can perform the following delegator operations:
Add stake
Unlock stake
Reactivate stake
Withdraw stake
Validator flow
Delegation pool operations
See Delegation pool operations for the correct sequence of commands to run for the below flow.
Operator deploys validator node
Run command to get delegation pool address
Operator connects to the network using pool address derived in step 2
Owner initializes the delegation pool and sets operator
Delegators can add stake at any time
When the delegation pool reaches 1M EDS, the operator can call endless node join-validator-set to join the active validator set. Changes will be effective in the next epoch.
Validator validates (proposes blocks as a leader-validator) and gains rewards. Rewards are distributed to delegators proportionally to stake amount. The stake will automatically be locked up for a fixed duration (set by governance) and automatically renewed at expiration.
At any point, if the operator wants to update the consensus key or validator network addresses, they can call endless node update-consensus-key or endless node update-validator-network-addresses. Similar to changes to stake, the changes to consensus key or validator network addresses are only effective in the next epoch.
Delegators can request to unlock their stake at any time. However, their stake will only become withdrawable when the delegation pool lockup expires.
Validator can either explicitly leave the validator set by calling endless node leave-validator-set or if their stake drops below the min required, they would get removed at the end of the epoch.
Joining the validator set
Participating as a delegation validator node on the Endless network works like this:
Operator runs a validator node and configures the on-chain validator network addresses and rotates the consensus key.
Owner initializes the delegation pool.
The validator node cannot sync until the delegation pool becomes active. The delegation pool becomes active when it reaches 1M EDS.
Operator validates and gains rewards.
The stake pool is automatically locked up for a fixed duration (set by the Endless governance) and will be automatically renewed at expiration. Commissions are automatically distributed to the operator as rewards. The operator can unlock stake at any time, but cannot withdraw until the delegation pool’s lockup period expires.
Operator must wait until the new epoch starts before their validator becomes active.
Joining the validator set
For step-by-step instructions on how to join the validator set, see: Joining Validator Set.
Automatic lockup duration
When the operator joins the validator set, the delegation pool's stake will automatically be locked up for a fixed duration that is set by the Endless governance. Delegators will follow the delegation pool's lockup cycle.
Automatic lockup renewal
When the lockup period expires, it will be automatically renewed, so that the validator can continue to validate and receive the rewards.
Unlocking your stake
Delegators can unlock stake at any time. However, the stake will only become withdrawable after the delegation pool's lockup period expires. Unlocked stake will continue earning rewards until the stake becomes withdrawable.
Resetting the lockup
Lockup cannot be reset.
Rewards
Rewards for delegated staking are calculated by using:
The rewards_rate, an annual percentage yield (APY), i.e., rewards accrue as a compound interest on your current staked amount.
Delegator stake
Validator rewards performance
See Computing delegation pool rewards
Last updated